We unleash your business potential by maximize the business innovation.
Send EmailE307, Alpha Tocopherol Acetate, D-alpha-Tocopherol, Vitamine E, Vitamin E Acetate, Naturel Vitamine E, 58-95-7, 59-02-9
🧬 Vitamin E Forms – CAS Comparison
| CAS No | Compound Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 59-02-9 | D-alpha-Tocopherol | Natural, biologically active form of Vitamin E; sensitive to oxidation and light |
| 58-95-7 | Vitamin E Acetate | Stabilized esterified form; longer shelf life, widely used in cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals |
🧪 Technical Breakdown – D-alpha-Tocopherol vs. Tocopheryl Acetate
| Parameter | D-alpha-Tocopherol (CAS 59-02-9) | Tocopheryl Acetate (CAS 58-95-7) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C₂₉H₅₀O₂ | C₃₁H₅₂O₃ |
| Molecular Weight | 430.71 g/mol | 472.74 g/mol |
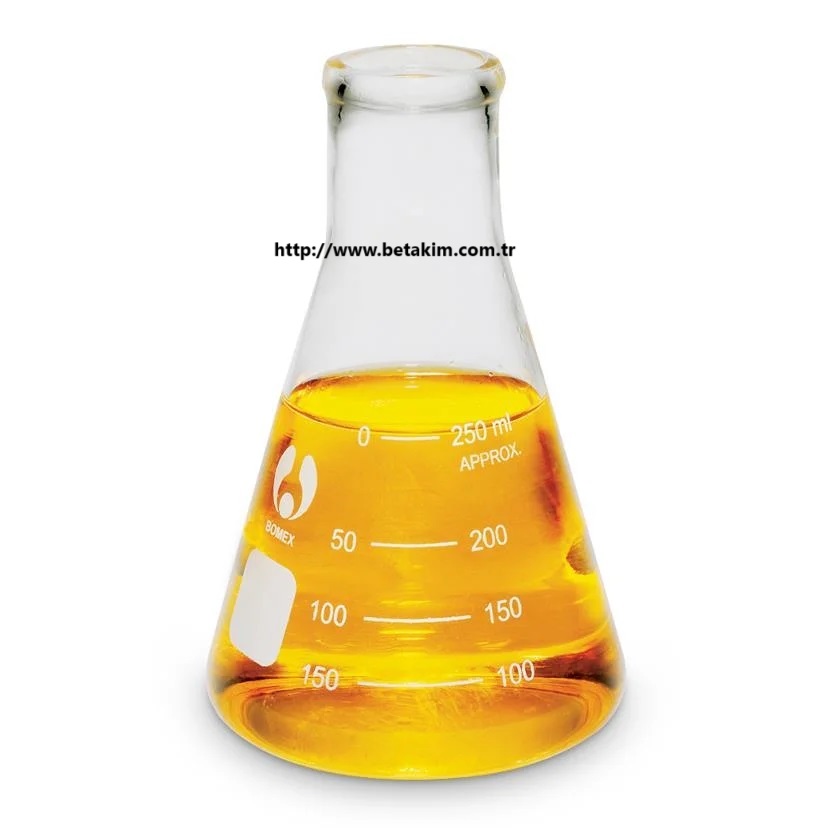
| Physical Form | Viscous yellow/brown oil | Clear to amber oily liquid |
| Solubility | Oil-soluble; insoluble in water | Oil-soluble; insoluble in water |
| Oxidation Sensitivity | High | Low (more stable) |
| Biological Activity | Immediate antioxidant activity | Requires hydrolysis to become active |
| Shelf Life | Shorter; sensitive to light & heat | Longer; resistant to oxidation |
| Common Applications | Nutraceuticals, premium supplements | Cosmetics, food additives, pharma |
| E Number | E307 | E307 |
🌿 Application Notes
-
D-alpha-Tocopherol is preferred in high-potency vitamin formulations where bioactivity is critical.
-
Vitamin E Acetate is favored in topical creams, emulsions, and fortified food products due to its stability.
Both forms convert into active Vitamin E in the body, but their formulation suitability depends on processing conditions, desired shelf life, and delivery method.
CAS number 59-02-9 corresponds to Vitamin E, specifically the compound D-alpha-Tocopherol — the most biologically active form of Vitamin E.
🧪 Technical Profile – D-alpha-Tocopherol (Vitamin E)
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| CAS No | 59-02-9 |
| Chemical Name | D-alpha-Tocopherol |
| Molecular Formula | C₂₉H₅₀O₂ |
| Molecular Weight | 430.71 g/mol |
| Physical Form | Light yellow to brown viscous oil |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water; soluble in oils, acetone, ethanol, methylene chloride |
| Melting Point | 2.5–3.5 °C |
| Boiling Point | 200–220 °C @ 0.1 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 253 °C |
| Density | ~0.95 g/mL @ 25 °C |
| Stability | Sensitive to light and air; store under inert gas below 15 °C |
| HS Code | 29362800 |
🌿 Production Overview
Vitamin E is typically synthesized via:
-
Condensation of Trimethylhydroquinone (TMHQ) with Isophytol
-
Catalyzed under acidic conditions to form alpha-Tocopherol
-
Purified via vacuum distillation and stabilized as acetate or succinate esters for shelf life
Natural sources include sunflower oil, safflower oil, wheat germ, and palm oil.
⚙️ Applications
| Sector | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Food | Antioxidant, shelf-life extender, nutritional fortification |
| Pharmaceuticals | Prevents oxidative stress, supports reproductive and neurological health |
| Cosmetics | Anti-aging, skin barrier protection, moisturizing agent |
| Animal Feed | Growth promoter, fertility support, antioxidant |
| Biotech | Cell culture media additive |
🏷️ Synonyms & Trade Names
-
D-alpha-Tocopherol
-
(+)-α-Tocopherol
-
Vitamin E (natural form)
-
RRR-alpha-Tocopherol
-
Tocopherol Type V
-
Antisterility Vitamin
-
E307 (food additive code)
Would you like me to prepare a sourcing comparison, COA request draft, or Betakim portfolio alignment for this compound? I can also contrast it with synthetic DL-alpha-Tocopherol if needed. 🧪📦📄
58-95-7
Alptekin, CAS No: 58-95-7 corresponds to Vitamin E Acetate, also known as alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate — a stabilized, oil-soluble form of Vitamin E widely used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and fortified food applications.
🧪 Vitamin E Acetate – Technical Specification
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate |
| CAS No | 58-95-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C₃₁H₅₂O₃ |
| Molecular Weight | 472.74 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear, pale yellow to amber viscous liquid |
| Solubility | Soluble in oils and organic solvents; insoluble in water |
| Melting Point | ~25–30 °C |
| Boiling Point | ~220 °C @ low pressure |
| pH | Not applicable (non-aqueous) |
| Stability | More stable than free tocopherol; resistant to oxidation |
| Shelf Life | 2+ years under nitrogen, cool, dry conditions |
| HS Code | 2936.28 |
⚙️ Applications
| Industry | Functions |
|---|---|
| Cosmetics | Anti-aging, skin barrier protection, antioxidant, moisturizer enhancer |
| Pharmaceuticals | Used in vitamin E supplements and topical formulations |
| Food | Fat-soluble antioxidant and nutritional fortifier |
| Feed | Vitamin E source for livestock and aquaculture |
🏷️ Synonyms & Trade Names
-
Tocopheryl Acetate
-
Alpha-Tocopherol Acetate
-
Vitamin E Acetate
-
E307 (food additive code)
-
Tocopheryl Ethanoate
-
Tokoferil Asetat (TR)
-
Alfa-Tokoferol Asetat
-
Tocopheryl Acetate USP / FCC
🔄 Related Products / Alternatives
| Compound | CAS No | Note |
|---|---|---|
| D-alpha-Tocopherol | 59-02-9 | Free tocopherol; less stable |
| DL-alpha-Tocopherol | 10191-41-0 | Synthetic racemic form |
| Tocopheryl Succinate | 4345-03-3 | Water-soluble derivative for drug delivery |
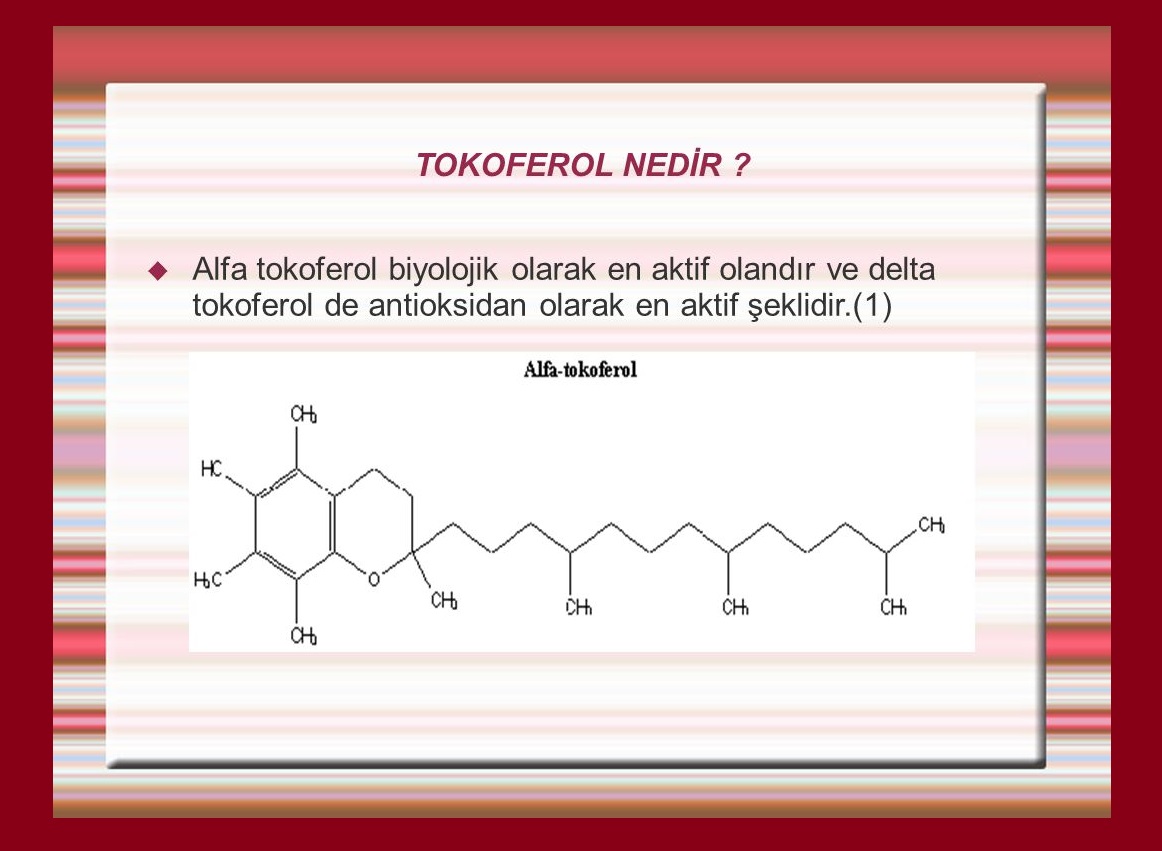
Molecular Formula (Vitamin E): C31H52O3
Molecular Weight: 472.70 g/mol
Chemical Name: Alpha-Tocopherol Acetate
CAS Number: 58-95-7
It has the strongest antioxidant properties among tocopherols. The antioxidant properties of this chemical compound are due to the phenolic hydrogen on the core.
Vitamins cannot be produced by the human body. However, they are compounds that are necessary for growth and maintenance. They are organic substances.
It is an indispensable part of skin care products. Nutrients taken into the body are converted into energy. While these nutrients are converted into energy, free radicals are formed. These are substances that are harmful to the body. Vitamin E Acetate is an important compound to prevent these free radicals.
It has the ability to protect Vitamin C from oxidation.
Other Names are as follows;
Tocopheryl Acetate
Alpha Tocopherol
Tocopherol
Tocopherol Acetate
How is Vitamin E Produced?
There is no detailed production information about this chemical compound.
What are its physical and chemical properties?
It has a white crystalline structure that has no odor.
Boiling Point is 363 °F.
Melting Point is 82 °F.
It dissolves less than 1 mg/mlt at 63 °F in solubility. It has water-soluble and oil-soluble forms.
Its density is around 0.95 gr/cm3.
Where are Vitamin E Used?
It is used in drugs produced as a dietary supplement for people with vitamin E deficiency.
Due to its oil-soluble antioxidant properties, it is used in some cosmetic products to inhibit free radicals. Here, it has protective effects on the cell membrane.
As a result of ultraviolet rays and peroxidation of lipids, the skin ages prematurely. In such skin care creams used to delay skin aging, an important compound, DL-Alpha Tocopheryl, is used.
The most important element among the working principle of the Vitamin E Acetate molecule is that it prevents peroxyl groups that cause lipid oxidation from spreading to other lipids and breaks the chain.
It can be used as a natural antioxidant to prevent tomato paste from spoiling in tomato paste production.
It is used by modifying it with Silicone in the production of creams that increase enzyme activity in the skin.
The chemical used to neutralize groups such as tocopherol radical is Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C).
It is used to meet the vitamin E needs of the skin with the topical use of Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate and tocopherol.
It is used as a preservative in stick cosmetic products, namely lipstick production, among its most common areas of use.
It is used as a preservative in dermatological pastes, preservative in Vaseline, preservative in hair styling, and preservative in the production of vital lubricants.
Vitamin E is used as a preservative compound in the production of carriers in therapeutic substances.
Human lips do not have a Stratum Corneum and an outer layer. For this reason, dryness and cracking of the lips occur in the winter months. Unlike other skin types, there are no sweat glands in the lip structure. For this reason, there is no other moisture source for the lip structure other than saliva. For this reason, dryness and cracking of the lips occur in the winter months. Lip balms are produced to prevent this. Alpha-Tocopherol Acetate is used in the production of lip balms.
It is used in very small amounts as a preservative in the production of wet wipes. However, a mixture of Phenoxyethanol/Ethylhexylglycerin is used.
Alpha Tocopherol is used in insect repellent sprays to nourish the skin after being sprayed onto the body.
Vitamin E (Alpha Tocopherol Acetate) is used as a preservative in the production of wound creams containing Sodium Fusidate as the active ingredient.
In the treatment of obesity, it helps both weight loss and liver disorders when used together with cold-pressed Black Cumin oil.
It is used in the production of nail strengthening compounds produced to strengthen brittle and weak nails.
It is used together with plant extracts in the production of eyelash nourishing lotion, which preserves the moisture of the eyelashes and helps strengthen the eyelashes.